Origin, Symptoms And Treatment Of Trench Mouth
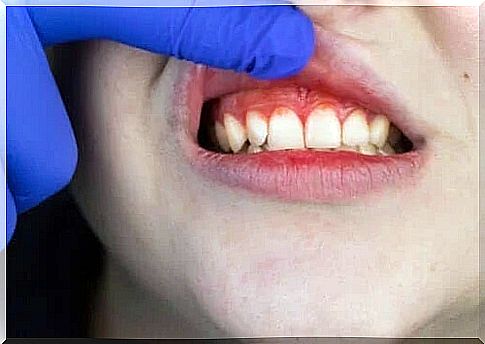
Trench mouth, also known as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG), is a rare disease today. He used to affect soldiers during the war because of the unhealthy conditions and habits they had to endure during conflicts. What are the origin, symptoms and treatment of the trench mouth?
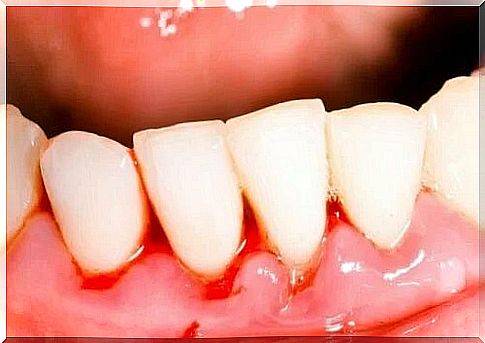
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis manifests itself as a painful infection in which the gums bleed due to papillary necrosis and general attack on oral health. According to studies, nowadays, the disease is associated with AIDS. Acquired immunodeficiency causes oral conditions in 90% of patients.
What causes trench mouth or acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis?
- The bacterial area is a large mass of bacteria with distinct morphologies and characteristics. At first, they are not necessarily harmful, but their excessive proliferation causes the disease.
- The area is rich in neutrophils, the most abundant leukocytes in the blood and the first to reach infectious foci. They are part of the pus and are present, in this case, in the bacterial area.
- The necrotic area is where cell death occurs. Spirochetes, bacteria with an elongated, helical shape, dominate this area.
- Spirochetal infiltration takes place in the last layer, in which there are no other types of bacteria.
What are the symptoms of the trench mouth?
The MSD manual states that the infection occurs suddenly, with pain and bleeding gums, plus excessive salivation. Some of the most common clinical signs are:
- Crater-type ulcers between the teeth
- Unpleasant taste in the patient’s mouth (some describe it as a metallic taste)
Possible complications
Given the difficulty of eating and living normally, other common complications are weight loss, dehydration and tooth loss. Bacteria can infiltrate the blood if a person with this condition ignores the symptoms, which leads to bacteremia.
The spread of the infection can be devastating because it affects several organs. In addition, septic shock may occur. This happens when the body reacts excessively and blood pressure drops.
Diagnosis of the trench mouth
As indicated by the scientific portal Drugs , physical examination is the first step in detecting the disease. The professional will look for ulcers, gray plaques around the teeth and the destruction of gingival tissue. The diagnosis is quick and not at all complicated.
Your doctor may order blood tests and x-rays. The latter are used to assess the damage caused by the infection, as the extent of the lesions is obvious. The approach will depend on the severity of the clinical picture.
When to seek medical help for trench mouth treatment?
Any kind of inflammation of the gums requires medical intervention and not all inflammations are caused by infections. However, you must rule out the disease in a timely manner. An oral infection can worsen considerably if not addressed in time, as bacteria can enter the bloodstream.
Trench mouth treatment
- Strict hygiene must be applied for the rest of your life to prevent recurrence.

Prevention of trench mouths
This is simple and is based on proper nutrition, proper oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist for checks. Professionals recommend that patients stay active and quit smoking.
In addition to all this, acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis has an important psychological component, as it is related to stress in many cases. Patients should seek help beyond the pharmacological field to address such pathologies.
The mouth of the trenches is almost gone
This disease is not as common as it used to be, as standards of personal hygiene continue to improve. You need to brush your teeth every day and go to the dentist regularly. He will be able to assess the possible risks to prevent the occurrence of this disease.