Symptoms And Treatment Of Bird Flu
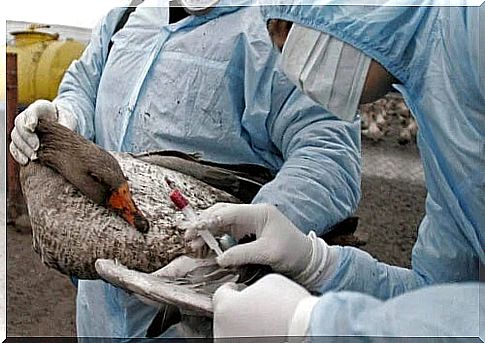
Viruses are infectious agents capable of invading most living things. Birds can be affected by influenza viruses that are transmitted between animals and then to humans. Want to know what the symptoms, causes and treatment of bird flu are? Read more!
Avian influenza is a disease caused by the influenza A virus. It is spread to birds through saliva, mucous and fecal secretions. However, cases have also been reported in humans.
Currently, more than 12 different strains of the virus have been identified, but only 3 of them have affected humans. However, ongoing mutations could increase the rate of human infection in the long run.
What are the symptoms of bird flu?
- precipitate

What is the cause?
The agent responsible for the occurrence of bird flu is the influenza A virus in its various mutagenic variants. The H5N1, H7N9 and H5N6 strains have been identified in humans, H5N1 being the most studied. More than 165 cases of bird flu were attributed to the latter between 2003 and 2006, with a mortality rate of over 50%.
Infection in humans occurs when the virus comes in contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose or mouth or by inhaling drops or dust containing viral particles. Moreover, direct contact with infected birds greatly increases the likelihood of infection.
Similarly, person-to-person transmission has been shown to be very low and generally occurs through family contact. The great adaptability of the virus to humans raises questions about the possible incidence of a new, more contagious strain in the future.
Risk factors
Diagnosis of bird flu
Identification of human avian influenza infection requires assessment of the symptoms and signs associated with laboratory tests. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends taking samples from the nose and throat in the first few days.
The extracted samples will be sent to specialized laboratories, where the agent will be identified by molecular testing or viral culture. Similarly, in patients with severe manifestations, samples should be taken from the lower respiratory tract to confirm the viral etiology.
In some patients, it is useful to determine antibodies against influenza A virus. To do this, two blood samples are taken; one at the onset of symptoms and another after 3 or 4 weeks. It should be noted that the results come after a few days.
The specialist may rely on imaging methods, such as chest radiography, to determine the involvement of the bronchopulmonary tree. Similarly, this test makes it possible to evaluate the therapeutic protocol to be followed.
Treatment of bird flu
The treatment of bird flu aims to alleviate the symptoms and eliminate the responsible viral agent. The use of antiviral inhibitors of neuraminidase is effective in some cases. These drugs block the release of the virus from infected cells and the colonization of the rest of the cells.
Most influenza A and B virus strains are sensitive to oseltamivir or Tamiflu®, peramivir and zanamivir or Relenza®. However, the CDC has reported some resistance to these drugs to mutations in H5N1 and H7N9 strains in Asian patients.
Similarly, therapy includes proper fluid replacement and the use of antipyretic and analgesic drugs to reduce the associated symptoms.
Recovery from avian influenza treatment
Prevention of bird flu
People who decide to visit countries at risk of bird flu infection should avoid open-air markets. In addition, poorly processed poultry products should not be consumed.
With regard to vaccines, the administration of immunization against seasonal influenza does not prevent the risk of contamination, but reduces the incidence of viral coinfection. The United States currently has a stockpile of vaccines against the H5N1 strain of Asian origin. However, vaccines would not be effective in the face of a possible mutation.
Avian flu infection should not be underestimated
The symptoms of bird flu are often diffuse and tend to be confused with those present in other forms of influenza. It is vital to go to the specialist in time to have a positive evolution of the disease.
Fatal complications can occur in some patients who do not receive timely bird flu treatment or are treated inadequately. If you have severe respiratory distress or experience worsening symptoms, go to the hospital as soon as possible.